Only when organisational and financial data are consistently managed using effective information systems can a business be successful. Due to accuracy and dependability, the majority of businesses have noticed a drift in the workflow process. Having the right information at the right time is essential in the commercial world, where every industry is centred around the Internet of Things.
How does Modern Business influence Information Systems?
Businesses that can develop new strategies and inventive tactics can thrive in the market and continue to meet client expectations in the face of the ongoing change and evolution of customer preferences and requirements.
Advantages of information system are as follows:
New Products and Services: Each company that wants to grow and have a solid handle on the future must have a Business Information System. An IS can aid in the study of independent processes and coordinate work operations. A firm has the right to understand how they develop, expand, and promote their products and services thanks to an information system.

Information Storage: To recognise issues and ultimately discover answers, all firms should keep a record of their actions. Business information systems make it easy to store operational data, revision history, communication logs, and documents. Manual data storage is expensive and time-consuming. The data is kept in a database by a sophisticated information system, making it simpler to locate the data.
Components of information systems
Hardware, software, data, connectivity, and people are almost all that are required for a contemporary workplace to run well. These elements are present in some way or another in almost every information system.
Hardware: Information systems’ physical hardware is composed of computers. Nowadays, this doesn’t only refer to the desktop or laptop computer in your office; we often have computers around, even when we’re not pounding away at our keyboards. Large volumes of data may be collected, stored, accessed, and easily managed on smartphones, tablets, and even smart watches.
Software: Without the programmes that operate in the background and instruct the hardware what to perform, computers are nothing more than glossy, black mirrors. There are two categories of softwares, System softwares and Appllication softwares.
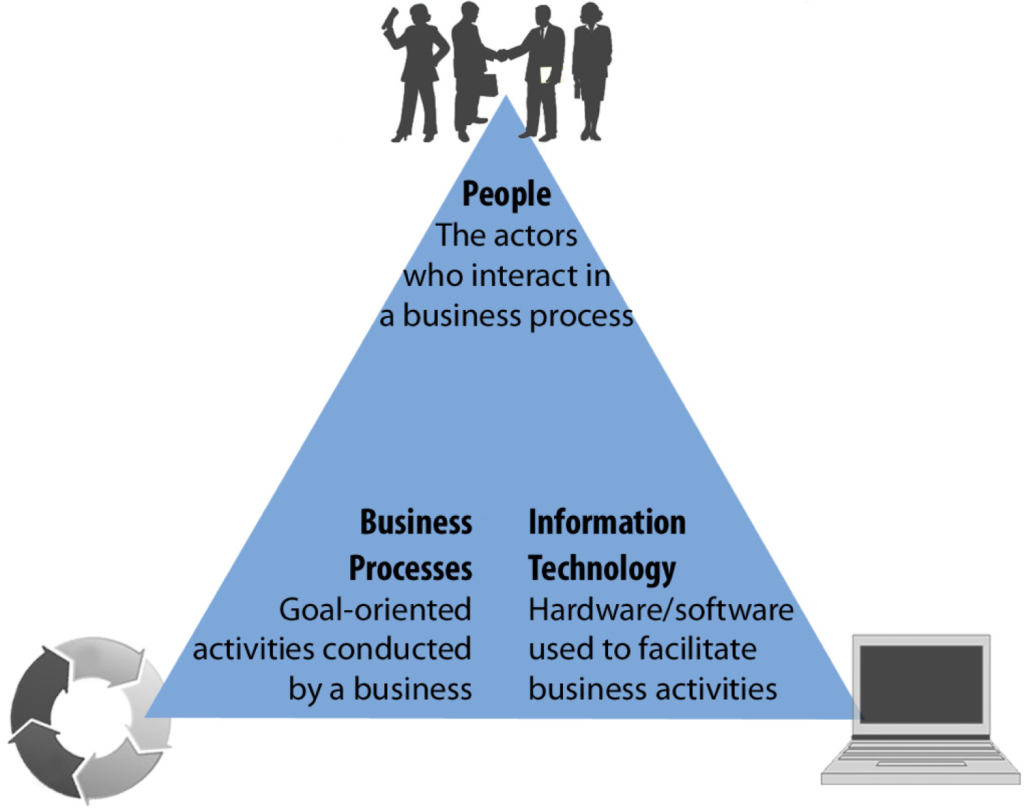
Data sources: Data is what gives information systems their “information.” Users and software can retrieve, analyse, and manipulate the both quantitative and qualitative information (data) that is stored in databases and data warehouses.
Telecommunications: Computers communicate with each other using telecommunications. The internet is probably the first thing that comes to mind, and you are right. Telecommunications, however, can be further divided.
Human resources: Robots are taking over many tiresome tasks due to automation, but we’re still a long way from a Westworld-style android takeover. Any information systems strategy requires human professionals who can comprehend and manipulate data.
Conclusion:
The foundation for making data-driven decisions is information systems. It enables businesses to make sense of vast amounts of data and utilise that knowledge to spot and fix procedural problems. Without it, your company would continue to suffer from the same outdated inefficiencies that slow it down.
Many schools provide information systems courses, in such courses a professional can learn about the planning and governance of major projects and programmes, as well as agile software development approaches.